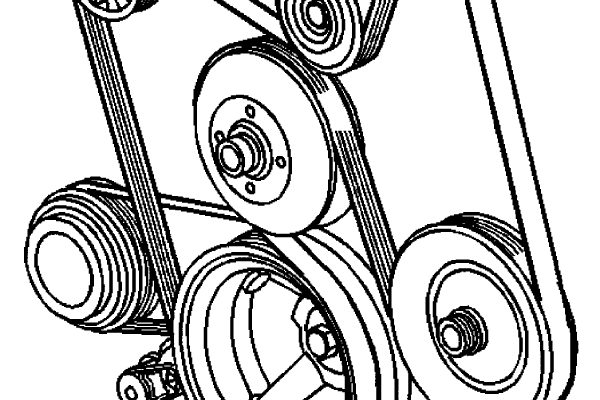
Introduction to Serpentine Belts
A serpentine belt is a critical car part. It is a long, snaking rubber belt. This belt drives multiple accessories on the engine. It powers the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioner compressor. In some cars, it also drives the water pump. The serpentine belt must stay tight and aligned. Understanding the serpentine belt diagram is essential for car maintenance, as it illustrates how this crucial component drives multiple engine accessories, ensuring they operate smoothly and efficiently.
A tensioner ensures this. Belts have a lifespan. They can wear out, become loose, or snap. Regular checks are key. They help avoid sudden car troubles. A damaged belt can lead to engine power loss. It can also stop accessory functions. The serpentine belt diagram aids in understanding its path.
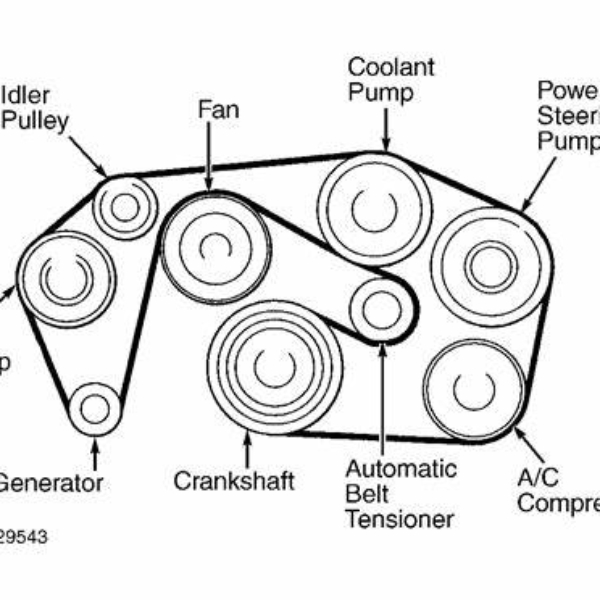
Every car is different. Refer to your car’s manual for the exact diagram. Keeping the serpentine belt in good condition is vital. It ensures smooth car function and prevents breakdowns. Understanding the serpentine belt diagram is essential for maintaining your vehicle, as it illustrates the belt’s path and helps you identify potential wear or damage, ensuring optimal performance and preventing unexpected breakdowns.
Key Functions of a Serpentine Belt
A serpentine belt fulfills several critical roles in a vehicle’s operation. Here are the key functions of a serpentine belt:
- Powers the Alternator: The serpentine belt drives the alternator. This device converts mechanical energy into electrical power. This power charges the battery and runs the car’s electrical systems.
- Runs the Power Steering: The belt also operates the power steering pump. This makes turning the steering wheel easier and allows for smooth vehicle control.
- Activates the Air Conditioning: Without the serpentine belt, the air conditioner’s compressor cannot function. The belt powers it, enabling cool air to circulate inside the car.
- Drives the Water Pump: In many cars, the serpentine belt also turns the water pump. The pump circulates coolant to maintain the engine’s temperature.
Overall, the serpentine belt is a hub of motion. It transfers the engine’s power to various parts needed for driving comfort and engine health.
Lifecycle of a Serpentine Belt
A serpentine belt’s lifespan is not indefinite. On average, it can last between 60,000 to 100,000 miles. That’s roughly 5 to 7 years. But its life can vary. Factors like vehicle make, belt quality, and driving conditions affect it. Extreme temperatures harm the belt. So do harsh chemicals, and oil or grease contamination. Regular checks are important. They help spot signs of wear and prevent a sudden break. It’s wise to inspect the belt at each service interval. Look for cracks, splitting, or fraying.
Also, check for a glossy or glazed appearance. These signs suggest the belt needs replacing. Some belts have tensioners that may need adjustments or replace over time. Unattended, these signs can lead to belt failure. If the belt breaks, the car can stop running. To avoid this, stay on top of maintenance. Replace the serpentine belt as needed to keep your car running well. Maintaining your car’s serpentine belt is crucial for preventing breakdowns; if you notice any glossy appearance or tension issues, it’s important to learn how to tighten serpentine belt properly and replace it when necessary to ensure smooth operation and longevity.
Indicators of Serpentine Belt Wear and Tear
To keep your car running smoothly, watch out for signs of serpentine belt wear. Regular checks can catch issues early. Here are common indicators that your serpentine belt may need attention:
- Loud Screeching Noise: A screeching sound from under the hood often means the belt is slipping.
- Visible Cracks or Splits: Check the belt for any cracks, splits, or signs of fraying. These issues suggest that the belt is weakening.
- Glazed or Shiny Appearance: A belt that looks glossy may be worn and at risk of slipping.
- Power Steering Problems: Difficulty steering can indicate a failing serpentine belt.
- Overheating Engine: If the belt drives the water pump, its failure can cause the engine to overheat.
- Warning Lights: Dashboard lights may turn on if the serpentine belt affects connected parts.
- Battery Issues: A weak or dead battery might result from a failing belt if it runs the alternator.
- Air Conditioning Malfunction: If the A/C stops working, it could be linked to belt damage.
Spotting these signs can help you address belt issues before they lead to bigger problems. Replace the belt promptly when wear is evident. This action can save you from unexpected breakdowns and high repair costs.
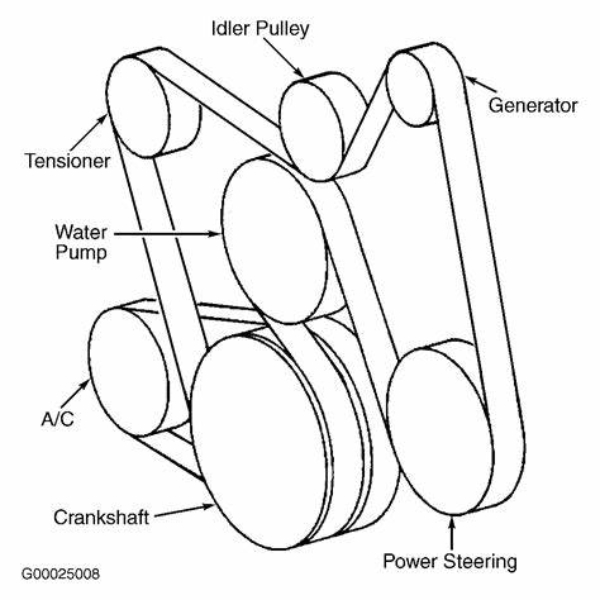
Consequences of Serpentine Belt Failure
Understanding the possible outcomes of a serpentine belt failure is critical for car owners. When a serpentine belt snaps or wears out, it can lead to a series of malfunctions and vehicle breakdowns. Below are the consequences that drivers may face:
- Loss of Power Steering: A failed serpentine belt stops the power steering pump. Steering becomes difficult, often with little warning.
- Failed Air Conditioning: The A/C compressor won’t work without the belt. This results in a loss of cool air inside the car.
- Overheated Engine: A broken belt can halt the water pump. This prevents coolant circulation, and the engine may overheat.
- Battery Drain: Without the belt, the alternator can’t charge the battery. The vehicle may not start, or electrical components may fail.
- Vehicle Stalling: Serious belt damage might cause complete vehicle stall, resulting in a potential roadside breakdown.
It’s important to note that these are not just minor inconveniences. An overheated engine could cause permanent damage. A sudden loss of steering could lead to a road accident. Thus, prompt attention to serpentine belt health is key to avoiding costly and dangerous outcomes.
Replacement Costs for a Serpentine Belt
When your serpentine belt needs replacement, costs can vary. The price of the belt itself usually ranges from about $25 to $75. However, the full cost includes labor. A professional mechanic might charge between $75 and $120 for labor. This depends on the car’s make and model. In total, expect to pay around $100 to $195 to replace your serpentine belt.
Some luxury cars have higher replacement costs. For these vehicles, the price can climb to between $200 and $600. Remember, belt tensioners or pulleys might also need replacing. This can add to the overall expense. Always get a detailed quote from your mechanic. Doing so helps avoid surprise costs. When dealing with luxury cars, it’s crucial to be aware of serpentine belt symptoms, as ignoring them can lead to costly replacements and added expenses for tensioners or pulleys. Always consult your mechanic for a thorough evaluation and detailed quote.
There are ways to save money. If you have the right skills and tools, consider a self-replacement. This choice cuts out labor costs. Yet, it’s crucial to be certain of your ability. Incorrect installation can lead to more problems. For accurate fitment, consult your car’s serpentine belt diagram. It’s a guide to proper installation.
In summary, plan for replacement costs accordingly. Keep in mind labor fees, potential additional parts, and your own mechanic skills. Regular belt checks can prevent sudden replacement needs and help budget for this maintenance.
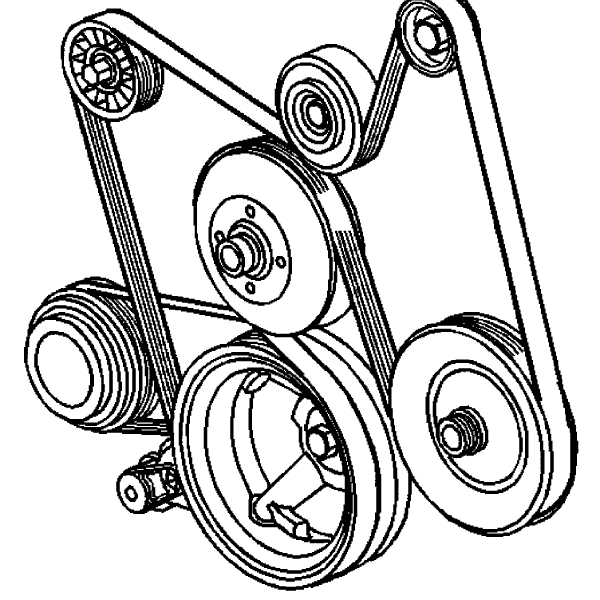
When to Seek Professional Replacement
Knowing the right time to seek professional replacement for your serpentine belt is crucial. Here are signs that it’s time to call a mechanic:
- Complicated Belt Pathway: If the serpentine belt diagram shows a complex path, a pro can handle it better.
- Noisy Tensioners or Pulleys: Should you hear unusual noises, a professional can diagnose if it’s the belt or related parts.
- Limited Experience: If you lack mechanic skills, it’s safer to get professional help.
- Proper Tensioning Issues: Correct belt tension is key. Mechanics have the right tools for it.
- Specialized Tools Needed: Some cars require specific tools for belt replacement that you might not have.
It’s important not to delay this service. A delay can lead to more car damage and higher costs. A trained mechanic will replace the belt efficiently and ensure your vehicle functions well.
Tips for Self-Replacement of Serpentine Belts
Replacing a serpentine belt on your own can save money. But it requires skill and caution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you do it safely:
- Get the right tools: You will need a set of wrenches and a serpentine belt tool. Sometimes, a screwdriver may also be necessary.
- Find the serpentine belt diagram: This is crucial. It guides you on the belt’s path. Check your owner’s manual or look for a sticker under the hood.
- Inspect the old belt: Before removing it, look for signs of wear. This helps you understand what to avoid with the new belt.
- Release tension: Use the serpentine belt tool to move the tensioner. This allows you to remove the old belt.
- Install the new belt: Follow the serpentine belt diagram closely. Make sure every pulley is engaged by the belt.
- Check alignment: Before finishing, ensure the belt sits properly on all pulleys. Misalignment can cause damage.
- Restore tension: Move the tensioner back into place. This secures the new belt.
- Double-check your work: Take a final look to confirm everything is correct. Start your engine and observe.
Remember, proper tension is key. Too tight or too loose can both cause issues. If you are not confident, seek a professional mechanic. They can replace the belt and ensure everything runs smoothly.